2025年12月13日Anthony.KimEnglish
Why Ontology Matters Again in the Era of LLMs
— Graph RAG, Knowledge Graphs, and Semantics-Based AI Architecture
Introduction
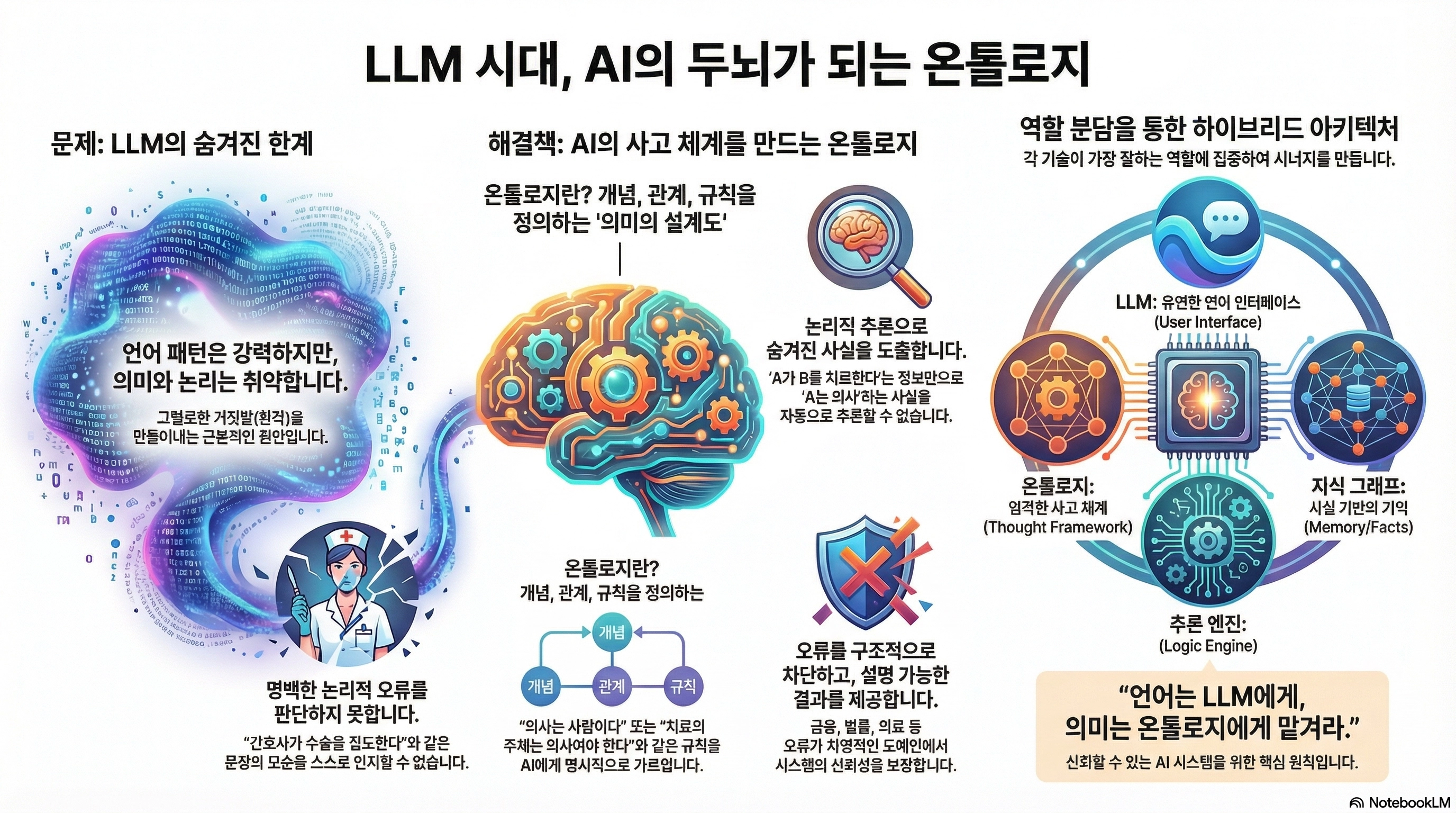
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has dramatically expanded the interface and scope of AI systems. However, behind the fluent natural language generated by LLMs, fundamental limitations still exist. The key point is that LLMs are strong in language patterns but inherently weak in semantics and logic.
To address this limitation, the concept of Ontology is regaining attention. In this article, we will systematically answer the following questions:
- What is an ontology, and what role does it play in AI?
- How is an ontology different from a knowledge graph?
- Can Graph RAG replace ontologies?
- Where should an ontology actually be positioned in LLM-based services?
1. What is Ontology: A 'Hierarchy of Meaning', Not Just Data
An ontology is a semantic model that explicitly defines the concepts, relations, and rules used in a specific domain. It does not merely store data or define structures; it prescribes "how to understand this world."
For example, in the medical domain, an ontology defines facts such as:
Doctor ⊆ Person- The subject of the
treatsrelation must be have aDoctortype. - A
Hospitalis anOrganization, not aPerson.
These definitions are common sense to humans, but for AI systems, they are rules that can never be known unless explicitly stated.
2. Why Ontology is Important in AI
2.1 Semantics-Based Reasoning
Ontologies enable AI to logically deduce facts that are not explicitly stated.
For example, suppose the following is given:
- A treats B.
- The domain of
treatsisDoctor.
Through ontology-based reasoning, the system can automatically deduce:
A is a Doctor. A is a Person.
Such reasoning is impossible with traditional machine learning or LLMs alone.
2.2 Consistency Verification and Error Detection
LLMs often generate plausible but incorrect statements (hallucinations). Ontologies serve as a mechanism to structurally block this.
Example:
- "A nurse performs surgery." → Violation of ontology rules → Immediately judged as an error.
In domains where errors are not tolerable, such as medicine, law, and finance, this is a decisive difference.
2.3 Explainable AI (Explainability)
Using ontologies and knowledge graphs, we can explain the logical path for an AI's judgment: "Why was this conclusion reached?"
This goes beyond simple user trust and is directly linked to issues of regulation, auditing, and accountability.
3. Ontology vs. Knowledge Graph: The Relationship Between Blueprints and Buildings
Ontologies and knowledge graphs are often used interchangeably, but their roles are clearly different.
| Category | Ontology | Knowledge Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Core Role | Definition of concepts, meanings, rules | Actual facts and instances |
| Nature | Abstract, stable | Concrete, dynamic |
| Example | "Doctors are people" | "Dr. Lee is a doctor" |
To use an analogy:
- Ontology is the code of law or a blueprint.
- Knowledge Graph is the case law or the actual building.
A knowledge graph is merely connected data without an ontology, and an ontology only connects to reality through a knowledge graph.
4. Standard Architecture in the LLM Era: Where Does Ontology Fit?
The most stable structure in modern AI services is a hybrid architecture like the following:
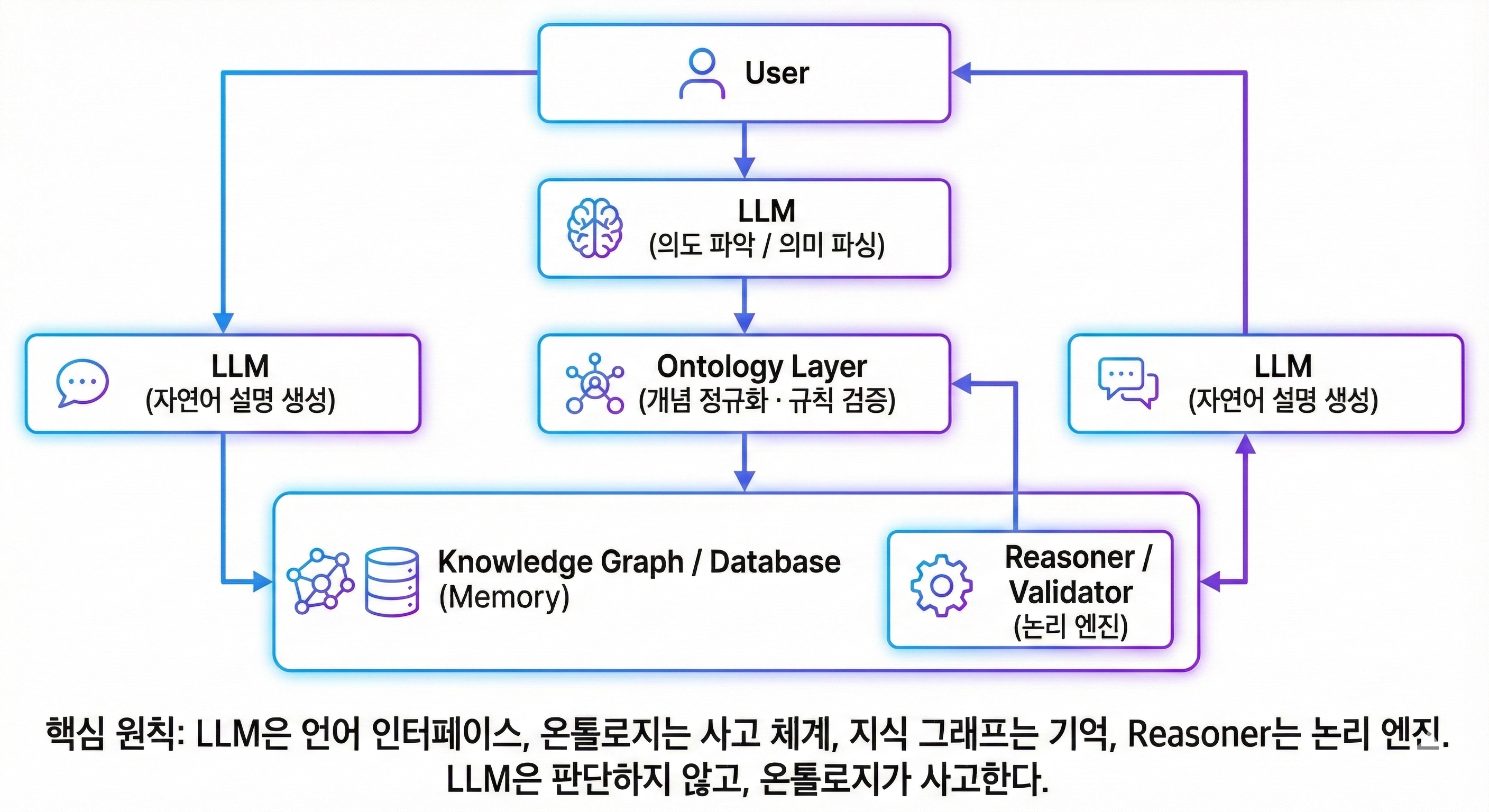
The core principles in this structure are clear:
- LLM is the Language Interface.
- Ontology is the System of Thought.
- Knowledge Graph is the Memory.
- Reasoner is the Logic Engine.
The LLM does not judge; the ontology thinks.
5. Can Graph RAG Replace Ontology?
To state the conclusion first:
Graph RAG can 'utilize' ontologies, but it cannot 'replace' them.
5.1 What Graph RAG Does Well
- Entity and relationship-based search
- Query expansion using concept schemas
- Exploration of related documents and nodes
In these areas, Graph RAG can perform part of the role of a lightweight ontology.
5.2 Limitations of Graph RAG
However, Graph RAG essentially does not inherently provide:
- Automated reasoning based on formal logic
- Consistency checking
- Rule violation detection
In other words, Graph RAG can "navigate following meanings," but it cannot "judge whether the meaning is logically correct."
5.3 Realistic Optimal Solution
The structure most commonly adopted in practice is:
Graph RAG
+ Lightweight Ontology (Type/Relation Definitions)
+ SHACL or Rule Engine
- Graph → Relation-based exploration
- Ontology → Meaning definition
- Rules/Constraints → Error blocking
6. When to Use Ontology
Must-Have Cases
- Complex domains
- Many rules and exceptions
- High cost of errors
- Explainability is required
→ Medical, Legal, Financial, Internal Knowledge Systems
Nice-to-Have / Not Necessary Cases
- Emotion/Creativity-centered
- Errors are tolerable
- Simple recommendation/conversation
Conclusion
LLMs made AI "speak," but Ontologies make AI "understand."
Graph RAG is a powerful tool, but The final responsibility for meaning and logic still lies with the ontology.
A truly trustworthy AI system is completed when the flexibility of LLMs and the rigor of ontologies are combined.
Leave language to the LLM, and leave meaning to the Ontology.
更多文章

In the AI-agent era, we believe what developers and enterprises need is not a comforting companion, but an equal partner that helps teams achieve outcomes. Here’s how we think about Caret and Caretive.

